Maximum Size subarray problem
Given an array nums and a target value k, find the maximum length of a subarray that sums to k. If there isn’t one, return 0 instead.
Note:
The sum of the entire nums array is guaranteed to fit within the 32-bit signed integer range.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1, -1, 5, -2, 3], k = 3,
return 4. (because the subarray [1, -1, 5, -2] sums to 3 and is the longest)
Example 2:
Given nums = [-2, -1, 2, 1], k = 1,
return 2. (because the subarray [-1, 2] sums to 1 and is the longest)
Algorithm
The brute force solution is straightforward, try all possible combinations:
for index i ~ (0, n):
for index j ~ (i, n):
if sum(i, j) == k
minLen = min(minLen, j - i + 1);
This algorithm takes O(n ^ 2) time, which is too slow.
The second solution I thought of was a sliding window algorithm.
while (right < boundary):
sum += nums[right++]
while (sum == target):
minLen = min(minLen, right - left)
sum -= nums[left++]
Sliding window does not work for this problem because:
- Skipped part of the window may also contribute to a maxSize subarray.
- Move right does not make the sum bigger, move left does not make the sum smaller. because number can be positive or negative.
A better solution is based on the following idea:
- sum(i, j) = sum(0, j) - sum(i)
- sum(0, i), sum(0, j) can be computed incrementally
The following diagram better illustrate the idea:
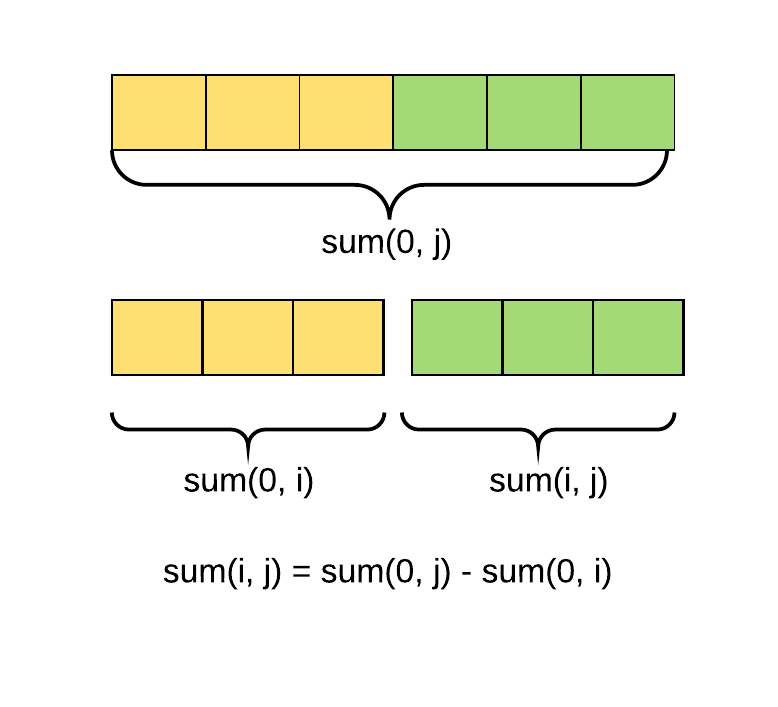
So we have the following algorithm:
for i ~ (0, n):
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + num[i]
gap = sum[i] - target
if gap in map:
maxWindow = Math.max(maxWindow, i - map(gap))
if sum[i] not in map:
map.put(sum[i], i)
Implementation
The following code implemented the algorithm above:
public int maxSubArrayLen(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int sum = 0, maxLen = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> sumIndex = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
if (sum == k) {
maxLen = i + 1;
} else if (sumIndex.containsKey(sum - k)) {
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i - sumIndex.get(sum - k));
}
if (!sumIndex.containsKey(sum)) {
sumIndex.put(sum, i);
} // not update index because we want max sum
}
return maxLen;
}- Runtime: O(n)